MY BLOGS
- HOME
- Open Source For You
- SCIENCE
- PHYSICS
- CSE
- PYTHON
- C
- C#
- Q#
- CONTEXTUAL ROBOTS
- DATA ANALYTICS
- MACHINE LEARNING
- ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
- QUANTUM COMPUTING
- PATENT
- PHD GUIDANCE
- GITHUB
- DATA SETS
- COINS LAB
- THYAGUAPPS
- THYAGU LEARNER
- COGNITIVE CLASS AI
- THYAGUCONTEXTDATA
- TENSOR FLOW
- AI NEWS
- SIMPLILEARN
- AI CLUB
- IOT CLUB
- YOJANA
Saturday 30 June 2018
Wednesday 27 June 2018
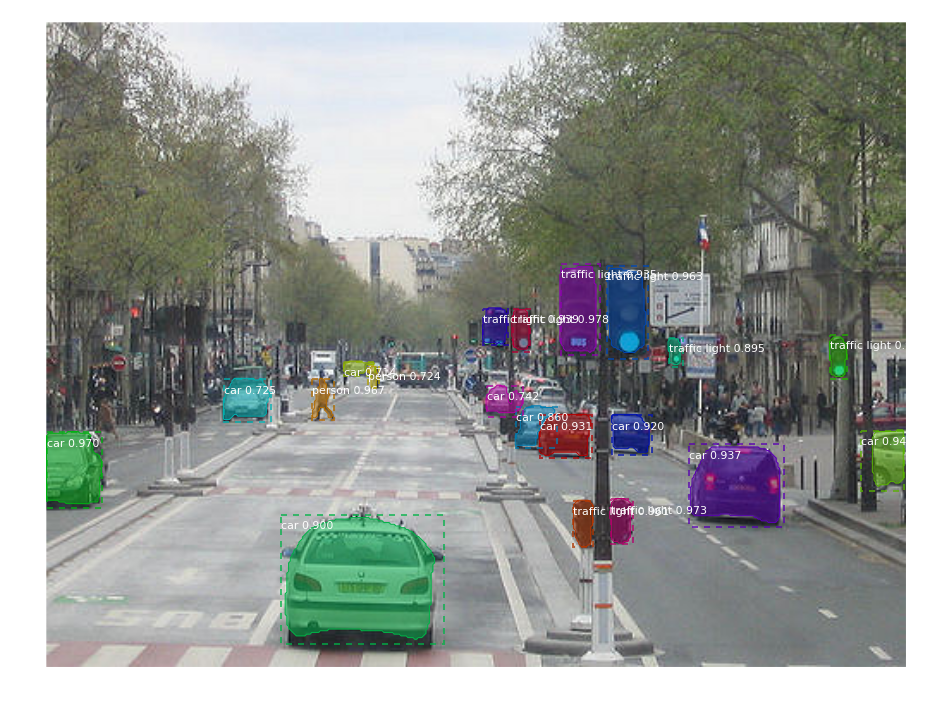
Machine Learning vs Rule-Based Content Management Systems
Source:
http://blog.quark.com/2018/01/machine-learning-vs-rule-based-content-management-systems/
http://blog.quark.com/2018/01/machine-learning-vs-rule-based-content-management-systems/
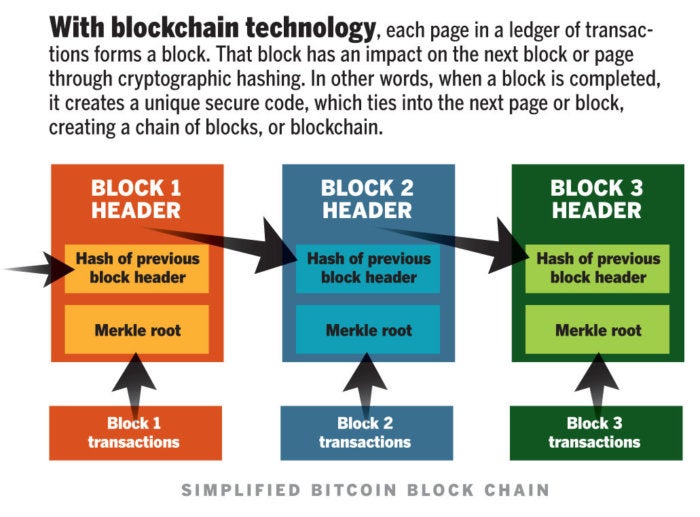
Karthik Guruswamy, Data Scientist at Teradata, got us thinking about how machine learning is replacing rule-based systems in how we manage and use enterprise content, knowledge, and ideas. Karthik explains that for the last 25 years rule-based systems have typically been built along the forms of:
If X then do Y or else if P then do Q etc.
These types of rules are extremely easy to understand and easy to code. But, Karthik points out, things quickly get out of hand: “When a system gets operationalized, one starts with 100 scenarios with 100 rules to handle it. As time goes by we encounter more and more exceptions and start making more rules to keep exceptions under control. What’s wrong with this approach? Think US Tax Code – things get unwieldy and cumbersome over time.”
Rule-Based Content Management Systems
Content Management Systems have traditionally been dumb boxes that were designed to make it easy to store information and didn’t give much through to information retrieval. In the past few years rule-based content management systems have emerged – think a system that leverages location software to prevent a rep from accessing content that is not intended for a specific geography, or a system that includes a quasi programming language that admins use to build Access Authentication Authorization (AAA) rules to manage content. While well intentioned, both the traditional storage approach and now the rules based approach to sales content management have fallen flat and fail to solve the problem of delivering “the right information at the right time in the right format and in the right place to assist in moving a specific sales opportunity forward.”
Content Management and Sales Enablement
Many companies built and implemented a well thought out place for sales reps to find content. These solutions provided some small scale value but the problem sales reps face of finding the right information at the right time still exists because, as is always the case, different repositories, portals, and tools across the enterprise house the diverse and relevant pieces of content designed and used for very specific purposes, and it’s not possible to keep these single-repository solutions updated with all the most relevant content, and it’s also not possible to keep the system up to date with all the rules required to manage content access.
Guruswamy says “rules based systems are like dinosaurs in the big data world – the volume, velocity, complexity and variety of data makes it near impossible to do well. Increasing number of false positives and negatives can wreak havoc in your operational systems with no useful actionable results …”
If Keeping Up To Date With All The Rules Doesn’t Kill You, The False Positives Certainly Will
Now think about this in relation to sales content management. Rule-based system will work only if you know all the situations under which decisions can be made. But how is this possible in today’s complex world where buyers expect messaging, collateral, and presentations, really everything they hear or see, to be tailored to their specific industry, geography, company size, solution needs, etc? It’s not possible.
Rule-based systems try to predict all the content needed within a sales cycle, so reps aren’t forced to go hunting for the right stuff (or forced to create their own).
In a rule-based system a set of content might be loaded into a CRM, with relevant content attached at each stage of the selling cycle. This simplifies things for the rep: as she promotes an opportunity to the next stage, the relevant content for that stage is attached right there at the opportunity level. She can grab it for her next meeting without having to go search or email people asking for the right content.
But what happens when the rep faces a scenario they haven’t encountered before? Unique situations arise all the time in B2B sales, it’s not possible to predict everything, and today’s world can’t be simplified down to personas. Rule-based systems can’t handle this and force reps into using material that was designed for a completely different use case. If a rep is forced to do or use something, and if the results aren’t perfect, a rep will never use the solution again. If programming an infinite number of rules doesn’t get you, it’s the false positives that will kill your prescriptive approach to sales content management.
Machine learning – A new way
Modern technologies allow a new approach:
- Synch with real world content and data, and then prompt users with the most relevant content based on explicit signals such as search and implicit signals such as CRM activity.
Rather than re-creating another repository, a modern machine-learning approach would connect to all existing repositories and auto-discover content and metadata. This approach abstracts the complexity away from implementation, keeping every underlying content repository in sync in real time, drastically reducing the amount of manual effort required to maintain the solution compared to a rule-based repository approach.
Most importantly, this abstraction of the complexity away from the user, while providing more relevant content recommendations – drawing on a larger corpus of content with a smarter relevance engine – means users actually use the platform and can count on the results.
Conclusion
Very simply put – the benefits of a machine learning approach to content management trump rule-based because of it’s convenience, scalability and low operational cost – especially as content these days is unstructured, structured and semi-structured. Machine Learning has the ability to measure effectiveness and improve itself by changing algorithms or tweaking the weighting of different inputs that feed into the algorithms.
To put it in Guruswamy’s words “Machine Learning system removes the manual task of classifying and tweaking rules each time. Fixing rules manually over time is like fixing bugs as the code gets bigger – problem becomes harder like adding to a house of cards.”
ಭೂತ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆಯಲ್ಲ; ಯಂತ್ರ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆ
Source : https://vijaykarnataka.indiatimes.com/edit-oped/columns/machine-learning/articleshow/63960703.cms

ನಿಮಗೆ ನೆನಪಿರಲಿ, 2018ರಲ್ಲಿ ಇಂಟರ್ನೆಟ್ ಬಳಸಿ ಶೋಧಾಕಾರ್ಯಚರಣೆ ಮಾಡುವವರ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆ 400 ಕೋಟಿ. ಪ್ರತಿ ಸೆಕೆಂಡ್ಗೆ ಏನಿಲ್ಲವೆಂದರೂ 40 ಸಾವಿರ ಸರ್ಚ್ಗಳ ಸಂಸ್ಕರಣೆ ನಡೆಯುತ್ತಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ದಿನವೊಂದಕ್ಕೆ 350 ಕೋಟಿ. ವರ್ಷಕ್ಕೆ 1.2 ಲಕ್ಷ ಕೋಟಿ. ಪ್ರತಿವರ್ಷ ಮನುಷ್ಯ ಸಂಕುಲ ಆನ್ಲೈನ್ನಲ್ಲಿ ವ್ಯಯಿಸುವ ಕಾಲವನ್ನು ಒಟ್ಟು ಮಾಡಿದರೆ ಒಂದು ಶತಕೋಟಿ ವರ್ಷವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ! ಇದರ ಅರ್ಥ ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬರ ಹುಡುಕಾಟದ ಜಾಡು ಹಿಡಿದು ಅವರು ಹೀಗೆ ಎಂದು ಕಣಿ ಹೇಳುವುದಕ್ಕೆ ಎಷ್ಟೊಂದು ಕಷ್ಟ ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಊಹೆ ಮಾಡಿ. ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಒತ್ತಾಸೆಯಿಂದ ಈ ಅಗಾಧ ದತ್ತಾಂಶಗಳನ್ನು ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಿಸಬಹುದು. ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ನ ಬಳಕೆ ಮತ್ತು ಅನ್ವಯದ ಸಾಧ್ಯತೆಗಳು ಹೆಚ್ಚುತ್ತಲೇ ಸಾಗುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಮನುಷ್ಯ ಶ್ರಮದ ಯಾಂತ್ರೀಕರಣ, ಸಂಪರ್ಕ ವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆಯ ನವೀಕರಣ, ನಿತ್ಯದ ಕೆಲಸಗಳಲ್ಲ್ಲಿ ಇದರ ಪಾತ್ರ ಅಗಾಧವಾಗಿದೆ. ಇದನ್ನು ಪವಾಡ ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯುವವರು ಎಷ್ಟು ಮಂದಿ ಇದ್ದಾರೋ ಇದನ್ನೊಂದು ಪ್ರಳಯಸ್ವರೂಪಿ, ಗಂಡಾಂತರಕಾರಿ ಎನ್ನುವವರು ಅಷ್ಟೇ ಮಂದಿ ಇದ್ದಾರೆ. ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟ ವಲಯಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಪ್ರಭಾವವನ್ನು ತಿಳಿದರೆ ಇದರ ಕುರಿತು ಅಂದಾಜು ಸಿಗುತ್ತದೆ.
ಶಿಕ್ಷ ಕರಿಗೆ ನೆರವು
ಶಿಕ್ಷ ಕರಿಗೆ ತರಬೇತಿದಾರ, ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಕ, ಸಮಾಲೋಚಕ, ಮಾರ್ಗದರ್ಶಕ, ತೀರ್ಪುಗಾರ- ಇತ್ಯಾದಿ ಕೆಲಸಗಳ ಕೋಡುಂಟು. ಸದ್ಯಕ್ಕೆ ಯಾವ ಗಣಕ, ರೊಬಾಟ್ ಕೂಟ ಈ ಕಾರ್ಯಗಳಿಗೆ ಸರಿಸಾಟಿಯಾಗಿಲ್ಲ. ಆದರೆ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಮೂಲಕ ಇವುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಕೆಲವೊಂದು ಕಾರ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತ(ಆಟೋಮೇಟೆಡ್)ಗೊಳಿಸಬಹುದು. ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಯೊಬ್ಬರ ಕಲಿಕಾ ಯೋಜನೆಯನ್ನು ಇಂಥದ್ದೇ ಎಂದು ನಿರ್ಧರಿಸುವ ರೀತಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಗಣಕವನ್ನು ರೂಪಿಸಬಹುದು. ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಯ ಅಗತ್ಯವನ್ನು ಕಂಡುಕೊಳ್ಳಬಹುದು. ಗಣಕದ ಕ್ರಮಾವಳಿ (Algorithm) ಯಿಂದ ಪರೀಕ್ಷೆಗಳ ಫಲಿತಾಂಶವನ್ನು ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಣೆಗೆ ಒಳಪಡಿಸಬಹುದು. ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಯೊಬ್ಬನ ಹಾಜರಿ ಮತ್ತು ಆತನ ಶೈಕ್ಷ ಣಿಕ ಸಾಧನೆಯ ಚರಿತ್ರೆಯ ವಿವರಗಳ ಮೂಲಕ ಆತನ ಜ್ಞಾನದ ಕೊರತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ನ್ಯೂನತೆಗಳನ್ನು ಕಂಡು ಹಿಡಿಯಬಹುದು. ಇದರಿಂದ ತರಗತಿ ಕೋಣೆ ಶಿಕ್ಷಕ ರಹಿತವೇನೂ ಆಗದು. ಆದರೆ ಬೋಧನೆ ಮತ್ತು ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ಪರಿಸರವನ್ನು ಖಂಡಿತ ಸುಧಾರಿಸಬಹುದು. ಶಿಕ್ಷ ಕ ಮತ್ತು ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳ ಹೊರೆಯನ್ನು ಹಗುರಗೊಳಿಸಬಹುದು.
ಕಾನೂನು ತಜ್ಞರ ಕೆಲಸಗಳ ಒತ್ತುವರಿ
ಕಾನೂನು ಮತ್ತು ನ್ಯಾಯಿಕ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ಅನ್ನು ಅವಲಂಬಿಸುತ್ತಿವೆ. ಅದರಲ್ಲೂ ದತ್ತಾಂಶ ಆಧಾರಿತ ಪ್ರಕರಣಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಅನಿವಾರ್ಯತೆಯನ್ನು ಕಂಡುಕೊಂಡಿವೆ. ಅಮೆರಿಕದ ಭಾರಿ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆ ಜೆ.ಪಿ.ಮೊರ್ಗನ್, ಕಂಟ್ರೋಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್ (ಕಾಯಿನ್) ಎನ್ನುವ ತಂತ್ರಾಂಶವನ್ನು ಬಳಸುತ್ತದೆ. ಇದರ ಮೂಲಕ ಹಿಂದಿನ ಪ್ರಕರಣ ಮತ್ತು ದಾಖಲೆಗಳನ್ನು ಕೇವಲ ಸೆಕೆಂಡ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಪರಾಮರ್ಶೆ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಇದು ಒಂದು ಸೆಕೆಂಡ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಮಾಡುವ ಕೆಲಸ, ಮನುಷ್ಯ ಶ್ರಮ ಉಪಯೋಗಿಸಿ ಮಾಡಿದರೆ 3.60.000 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು ಬೇಕಾಗುತ್ತದೆ! ಇದರಿಂದ ವಕೀಲರೇನು ಕೆಲಸ ಕಳೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ನಿಂದ ಪ್ರಕರಣಗಳನ್ನು ಕ್ಷಿಪ್ರವಾಗಿ ಅರ್ಥಮಾಡಿಕೊಳ್ಳಬಹುದು, ಅವುಗಳನ್ನು ತ್ವರಿತವಾಗಿ ವಿಲೇವಾರಿ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಲಕ್ಷಾಂತರ ಪ್ರಕರಣಗಳು ಧೂಳು ತಿನ್ನುತ್ತಿರುವ ನಮ್ಮ ನ್ಯಾಯವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಇಂಥ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನದ ಅಳವಡಿಕೆಯ ಖಂಡಿತ ಇದ್ದೇ ಇದೆ. ಇದರಿಂದ ಆಗುವ ಸಾಮಾಜಿಕ, ಆರ್ಥಿಕ ಪರಿಣಾಮಗಳು ಅಗಾಧ. ನಮ್ಮ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯಗಳು ಈ ಹಾದಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಸಾಗುವ ಅನಿವಾರ್ಯತೆ ಇದ್ದೇ ಇದೆ.
ಕುಶಲ ಮತ್ತು ಶ್ರಮಾಧಾರಿತ ವಲಯ
ಆಸೀಸ್ನ ಗಣಿಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತ ಟ್ರಕ್ಗಳು ಈಗಾಗಲೇ ಕಾರ್ಯನಿರತವಾಗಿವೆ. ಅಪಾಯದ ಸಾಧ್ಯತೆಗಳಿರುವ ವಲಯಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ತೀವ್ರಗತಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಯಾಂತ್ರೀಕರಣವಾಗುತ್ತಿರುವುದು ಎಲ್ಲರಿಗೂ ಗೊತ್ತೇ ಇದೆ. ತಾಲೂಕು ಕಚೇರಿಗಳಲ್ಲಿ, ಬ್ಯಾಂಕುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ, ಸೂಪರ್ ಮಾರ್ಕೆಟ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸ್ವಯಂಚಲಿ ಕಿಯೋಸ್ಕ್ಗಳು ಕಾಣಿಸುತ್ತಿವೆ. ಇವು ಏಷ್ಟೇ ಇರಲಿ, ಬರಲಿ ಮನುಷ್ಯನ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಗೆ ಸಾಟಿಯಲ್ಲ ನಿಜ. ಆದರೆ ಹಾಗೆಂದು ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನದ ಬಳಕೆಯ ವೇಗ ತಗ್ಗಿಲ್ಲ.
ಆರೋಗ್ಯ ರಕ್ಷಕ
ನಿತ್ಯದ ಆರೋಗ್ಯ, ಯೋಗಕ್ಷೇಮದ ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ದೊಡ್ಡ ಪಾತ್ರ ವಹಿಸುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಈಗಾಗಲೇ ರೋಗಿಗಳ ರೋಗವನ್ನು ಕ್ಷಿಪ್ರವಾಗಿ ಪತ್ತೆ ಮಾಡುವುದರಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನವನ್ನು ಬಳಸಲಾಗುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಇದರಿಂದ ಸಮಯ, ಹಣ ಉಳಿತಾಯವಷ್ಟೇ ಅಲ್ಲ ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸೆಯ ಮಟ್ಟವನ್ನು ಎತ್ತರಿಸಬಹುದು. ನಿಮ್ಮ ವಯಸ್ಸು, ಊಟ ತಿಂಡಿ ಪ್ರವೃತ್ತಿ, ಕೆಲಸದ ರೀತಿ ನೀತಿ, ವಂಶವಾಹಿ ಇತಿಹಾಸ- ಈ ಮಾಹಿತಿಗಳನ್ನು ಕಲೆ ಹಾಕಿ ನಿಮಗೆ ಸಂಭವನೀಯ ಆರೋಗ್ಯ ರಿಸ್ಕ್ಗಳು ಏನು ಬರಬಹುದು ಎಂದು ಗಣಕ ನಿಮಗೆ ಹೇಳಬಹುದು. ವಿವಿಧ ಬಗೆಯ ಕ್ಯಾನ್ಸರ್ ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಅದ್ಭುತ ಪಾತ್ರ ವಹಿಸುತ್ತಿದೆ.
2020ಕ್ಕೆ ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತ ನೌಕೆ
ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಮತ್ತು ಎಐ ಮುಂದಿನ ದಿನಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸಾರಿಗೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಕ್ರಾಂತಿಯನ್ನೇ ಉಂಟುಮಾಡಲಿದೆ. ನೌಕಾಯಾನ ಮತ್ತು ರೈಲ್ವೆ ಸಂಪರ್ಕ ಜಾಲದ ನಿಯಂತ್ರಣ ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣವಾಗಿ ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತವಾಗಲಿದೆ. ಸಾರ್ವಜನಿಕ ಸಾರಿಗೆ ಬಸ್ಗಳು ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತವಾಗಿ ಓಡಲು ಸಾಧ್ಯವೇ? ಈ ನಿಟ್ಟಿನಲ್ಲಿ ಚೀನಾ ದೃಢವಾಗಿ ಮುಂದುವರಿದಿದೆ. ರೋಲ್ಸ್ರಾಯ್, ಗೂಗಲ್ ಒಟ್ಟಿಗೆ ಸೇರಿ 2020ರ ವೇಳೆಗೆ ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತ ನೌಕೆಯನ್ನು ಅಭಿವೃದ್ಧಿ ಪಡಿಸಲಿವೆ. ಈ ನೌಕೆಯು ಗೂಗಲ್ ಕ್ಲೌಡ್ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಅನ್ನುಬಳಸಿ, ಸಮುದ್ರದಲ್ಲಿರುವ ವಸ್ತುಗಳನ್ನು ಕಂಡುಹಿಡಿಯಲು ದಾರಿ ಗುರುತಿಸಲು ಎಂಜಿನ್ಗೆ ನೆರವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಕೆಲವು ಕೆನಡಾದ ವಾಯುಯಾನ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳು ಪೈಲಟ್ ರಹಿತ ವಿಮಾನಗಳನ್ನು ಅಭಿವೃದ್ಧಿಪಡಿಸಲು ಸಾಕಷ್ಟು ಬಂಡವಾಳ ಹೂಡಿವೆ.
ನಿತ್ಯ ಜೀವನ ಲೀಲೆ
ಗೂಗಲ್ ಹೋಮ್ ಅಸಿಸ್ಟೆಂಟ್ನಂಥ ಯಂತ್ರಗಳು ಈಗಾಗಲೇ ನಮ್ಮ ಮನೆಗಳನ್ನು ಪ್ರವೇಶಿಸಿವೆ. ಕೇವಲ 5-10 ಸಾವಿರ ಬೆಲೆಯ ಚಾಕ್ರಿಯಂತ್ರಗಳು
ಸ್ಮಾರ್ಟ್ ಮನೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಲೈಟ್ ಹಾಕುವ, ಆಫ್ ಮಾಡುವ, ಬಾಗಿಲು ತೆರೆಯುವ ಬಂದ್ ಮಾಡುವ, ವಿವಿಧ ಕೆಲಸಗಳನ್ನು ನಿಮಗೆ ನೆನಪಿಸುವ ಕಾರ್ಯವನ್ನು ಮಾಡುತ್ತಿವೆ. ಫ್ರಿಡ್ಜ್, ವಾಷಿಂಗ್ಮೆಷಿನ್ಗಳನ್ನು ಎಲ್ಲೋ ದೂರದಿಂದಲೇ ಕಂಟ್ರೋಲ್ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಅದರೊಳಗೆ ಏನಿದೆ ಏನಿಲ್ಲ ಎಂದು ಇಣುಕಬಹುದು. ನೀವಿದ್ದಲ್ಲೇ ಅಂಗಡಿಯಾತನಿಗೆ ಆರ್ಡರ್ ಮಾಡಿ ಯಾರೂ ಇಲ್ಲದ ಮನೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಆ ಸರಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಇಳಿಸಿಕೊಂಡು ಅಂಗಡಿಯಾತನಿಗೆ ಟಾಟಾ ಹೇಳಬಹುದು. ಇದು ಭೂತ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆಯಲ್ಲ; ಯಂತ್ರ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆ.

ಭೂತ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆಯಲ್ಲ; ಯಂತ್ರ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆ /ವೆಂಕಟೇಶ್ ಕೆ
2018ರಲ್ಲಿ ಇಂಟರ್ನೆಟ್ ಬಳಸಿ ಶೋಧಾಕಾರ್ಯಚರಣೆ ಮಾಡುವವರ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆ 400 ಕೋಟಿ. ಪ್ರತಿ ಸೆಕೆಂಡ್ಗೆ ಏನಿಲ್ಲವೆಂದರೂ 40 ಸಾವಿರ ಸರ್ಚ್ಗಳ ಸಂಸ್ಕರಣೆ ನಡೆಯುತ್ತಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ದಿನವೊಂದಕ್ಕೆ 350 ಕೋಟಿ. ವರ್ಷಕ್ಕೆ 1.2 ಲಕ್ಷ ಕೋಟಿ. ಪ್ರತಿವರ್ಷ ಮನುಷ್ಯ ಸಂಕುಲ ಆನ್ಲೈನ್ನಲ್ಲಿ ವ್ಯಯಿಸುವ ಕಾಲವನ್ನು ಒಟ್ಟು ಮಾಡಿದರೆ ಒಂದು ಶತಕೋಟಿ ವರ್ಷವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ! ಇದರ ಅರ್ಥ ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬರ ಹುಡುಕಾಟದ ಜಾಡು ಹಿಡಿದು ಅವರು ಹೀಗೆ ಎಂದು ಕಣಿ ಹೇಳುವುದಕ್ಕೆ ಎಷ್ಟೊಂದು ಕಷ್ಟ ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಊಹೆ ಮಾಡಿ. ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಒತ್ತಾಸೆಯಿಂದ ಈ ಅಗಾಧ ದತ್ತಾಂಶಗಳನ್ನು ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಿಸಬಹುದು. ಏನಿದು ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್?
ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಎಂಬ ಶಬ್ದವನ್ನು ನೀವು ಕೇಳಿರಲಾರಿರಿ. ಇದು ನಿಮ್ಮ ಕಿವಿದೆರೆಗೆ ಬಿದ್ದಿದ್ದರೂ ಐಟಿಐನ ಫಿಟ್ಟರ್, ಟರ್ನರ್ನಂತೆ ಇದೂ ಒಂದು ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಇರಬಹುದು ಎಂದುಕೊಂಡು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ವಿವರಗಳನ್ನು ನಿಮ್ಮ ತಲೆಗೆ ಬಿಟ್ಟುಕೊಳ್ಳದೇ ಇರಬಹುದು. ಗಣಕವೊಂದು ಚೆಸ್ ಆಡುವುದು, ಲೆಕ್ಕ ಮಾಡುವುದು, ಇನ್ನಿತರ ಹತ್ತಾರು ನಡೆ ಮತ್ತು ಪ್ರತಿ ನಡೆಗಳ ಕಾರ್ಯವ್ಯೂಹ ನಿಮಗೆ ಚೆನ್ನಾಗಿ ಗೊತ್ತಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಎಂದಾಗಲಂತೂ ಟರ್ಮಿನೇಟರ್ ಸಿನಿಮಾ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಮನದ ಪರದೆ ಮೇಲೆ ಸುರಳಿ ಬಿಚ್ಚಿಕೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತದೆ. ರೊಬಾಟ್ಗಳ ಎಲ್ಲೆಡೆ ತಮ್ಮ ಬಾಹುಗಳನ್ನು ಚಾಚಿಕೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತಿರುವುದು ನಿಮಗೆ ತಟ್ಟಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಆದರೆ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ(ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್) ಅದರಲ್ಲೂ ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟವಾಗಿ ಹೇಳುವುದಾದರೆ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಕೇಡಲ್ಲ; ಭವಿಷ್ಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಎಂದೋ ಸಂಭವಿಸುವುದೂ ಅಲ್ಲ; ಅದು ಸದ್ಯದ್ದು. ಇದು ನಮ್ಮ ಜೀವನ, ಕೆಲಸ, ಸಂವಹನ, ವ್ಯಾಪಾರ, ವ್ಯವಹಾರ, ಪ್ರಯಾಣ ಎಲ್ಲದರ ಗೊತ್ತುಗುರಿಗಳನ್ನು ಬದಲಿಸಿಬಿಟ್ಟಿದೆ. ನಿತ್ಯಜೀವನದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ನಿರ್ದೇಶಿತ ಸಂಗತಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಡಿಕ್ಕಿ ಹೊಡೆಯುತ್ತಲೇ ಇರುತ್ತೇವೆ. ಆದರೆ ಅದೇನು ಎಂದು ಆಳವಾಗಿ ತಿಳಿದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವ ಗೋಜಿಗೆ ಹೋಗಿರುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಇಷ್ಟೆಲ್ಲ ಹೇಳಿದ ಮೇಲೂ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಎನ್ನುವುದನ್ನು ಇನ್ನಷ್ಟು ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟೀಕರಿಸಿ ತಿಳಿಯುವುದು ಅವಶ್ಯ.
ಎಂಎಲ್ (ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್) ಎಂಬುದು ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಯ ಒಂದು ಮೂಲಾಂಶ. ಚಾಲಕ ಶಕ್ತಿಯೂ ಹೌದು ಎನ್ನಬಹುದು. ಗಣಕವೊಂದು ತನಗೆ ತಾನೇ ಕಲಿತುಕೊಳ್ಳುವಂತೆ ಅದನ್ನು ಯೋಜಿಸಿರಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟ ಕೆಲಸಬೊಗಸೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ತನ್ನ ಸಾಮರ್ಥ್ಯವನ್ನು ಹೆಚ್ಚಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವ ಥರದಲ್ಲಿ ಅದರ ಸ್ವರೂಪವಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಬೇರುಮಟ್ಟದಲ್ಲಿ ಅದನ್ನು ನೋಡಿದರೆ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಎನ್ನುವುದು ದೊಡ್ಡ ದತ್ತಾಂಶಗಳು ಘ್ಕಿ(daಠಿa) ಗಳ ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಣೆಯಾಗಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಮಾಹಿತಿಯನ್ನು ತಾನೇ ತಾನಾಗಿ ತೆಗೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ನಿರ್ಣಯಗಳನ್ನು ರೂಪಿಸುವುದಕ್ಕೆ ಅದನ್ನು ಬಳಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದೇ ಆಗಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ನಿಮ್ಮ ಭವಿಷ್ಯವಾಣಿ, ಮುಂದಾಗಲಿರುವುದರ ಕುರಿತ ಕಥನಗಳು ಸರಿ ಇರಬಹುದು ತಪ್ಪೇ ಇರಬಹುದು ಅದನ್ನು ಗ್ರಹಿಸಲು ಮತ್ತು ನಿಖರವಾಗಿ ಪ್ರಿಡಿಕ್ಟ್ ಮಾಡಲು ಕಲಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. ಗೂಗಲ್, ಅಮೆಜಾನ್, ನೆಟ್ಫ್ಲಿಕ್ಸ್, ಫ್ಲಿಪ್ಕಾರ್ಟ್, ಮೈಂತ್ರಾ ದಂಥ ಆನ್ಲೈನ್ ವ್ಯಾಪಾರಿ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳು ಗಣಕದಲ್ಲಿ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಹುಡುಕಾಟ, ತಡಕಾಟ, ಖರೀದಿ, ಅದರ ಚರಿತ್ರೆಯ ಅಂಕಿ ಅಂಶ ಮತ್ತು ದಾಖಲೆಗಳನ್ನಿಟ್ಟುಕೊಂಡು ನಿಮಗೆ ಏನು ಇಷ್ಟ ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಊಹೆ ಮಾಡುತ್ತವೆ. ನಿಮ್ಮ ಅಭಿರುಚಿ, ಜೇಬಿನ ಸಾಮರ್ಥ್ಯ ಎಲ್ಲವನ್ನೂ ಅಳೆದು ತೂಗಿ ಇಂಥದ್ದೇ ಕೆಲ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳಿಗೆ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಖರೀದಿ ಚಹರೆಯನ್ನು ರವಾನಿಸುತ್ತವೆ. ಪ್ರತಿನಿತ್ಯ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಇನ್ಬಾಕ್ಸ್ಗೆ ಬಂದು ಬೀಳುವ ವಸ್ತು ಸಾಮಗ್ರಿ, ನಾನಾ ಥರದ ಸೇವೆಗಳ ಸೇವಾದಾತರ ವಿವರಗಳು ಹೇಗೆ ಬಂದಿರುತ್ತವೆ ಎಂದರೆ ಅದೆಲ್ಲವೂ ನೀವು ಜಾಲಾಡಿದ್ದರ ಫಲ (ಕರ್ಮಫಲವೂ ಇರಬಹುದು). ನಿಮ್ಮ ಮೌಸ್ನ ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಂದು ಚಲನೆ, ನಿಲುಗಡೆಯ ಮೇಲೆ ಹದ್ದಿನ ಕಣ್ಣಿರುತ್ತದೆ.
ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಎಂಬ ಶಬ್ದವನ್ನು ನೀವು ಕೇಳಿರಲಾರಿರಿ. ಇದು ನಿಮ್ಮ ಕಿವಿದೆರೆಗೆ ಬಿದ್ದಿದ್ದರೂ ಐಟಿಐನ ಫಿಟ್ಟರ್, ಟರ್ನರ್ನಂತೆ ಇದೂ ಒಂದು ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಇರಬಹುದು ಎಂದುಕೊಂಡು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ವಿವರಗಳನ್ನು ನಿಮ್ಮ ತಲೆಗೆ ಬಿಟ್ಟುಕೊಳ್ಳದೇ ಇರಬಹುದು. ಗಣಕವೊಂದು ಚೆಸ್ ಆಡುವುದು, ಲೆಕ್ಕ ಮಾಡುವುದು, ಇನ್ನಿತರ ಹತ್ತಾರು ನಡೆ ಮತ್ತು ಪ್ರತಿ ನಡೆಗಳ ಕಾರ್ಯವ್ಯೂಹ ನಿಮಗೆ ಚೆನ್ನಾಗಿ ಗೊತ್ತಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಎಂದಾಗಲಂತೂ ಟರ್ಮಿನೇಟರ್ ಸಿನಿಮಾ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಮನದ ಪರದೆ ಮೇಲೆ ಸುರಳಿ ಬಿಚ್ಚಿಕೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತದೆ. ರೊಬಾಟ್ಗಳ ಎಲ್ಲೆಡೆ ತಮ್ಮ ಬಾಹುಗಳನ್ನು ಚಾಚಿಕೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತಿರುವುದು ನಿಮಗೆ ತಟ್ಟಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಆದರೆ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ(ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್) ಅದರಲ್ಲೂ ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟವಾಗಿ ಹೇಳುವುದಾದರೆ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಕೇಡಲ್ಲ; ಭವಿಷ್ಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಎಂದೋ ಸಂಭವಿಸುವುದೂ ಅಲ್ಲ; ಅದು ಸದ್ಯದ್ದು. ಇದು ನಮ್ಮ ಜೀವನ, ಕೆಲಸ, ಸಂವಹನ, ವ್ಯಾಪಾರ, ವ್ಯವಹಾರ, ಪ್ರಯಾಣ ಎಲ್ಲದರ ಗೊತ್ತುಗುರಿಗಳನ್ನು ಬದಲಿಸಿಬಿಟ್ಟಿದೆ. ನಿತ್ಯಜೀವನದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ನಿರ್ದೇಶಿತ ಸಂಗತಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಡಿಕ್ಕಿ ಹೊಡೆಯುತ್ತಲೇ ಇರುತ್ತೇವೆ. ಆದರೆ ಅದೇನು ಎಂದು ಆಳವಾಗಿ ತಿಳಿದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವ ಗೋಜಿಗೆ ಹೋಗಿರುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಇಷ್ಟೆಲ್ಲ ಹೇಳಿದ ಮೇಲೂ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಎನ್ನುವುದನ್ನು ಇನ್ನಷ್ಟು ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟೀಕರಿಸಿ ತಿಳಿಯುವುದು ಅವಶ್ಯ.
ಎಂಎಲ್ (ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್) ಎಂಬುದು ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಯ ಒಂದು ಮೂಲಾಂಶ. ಚಾಲಕ ಶಕ್ತಿಯೂ ಹೌದು ಎನ್ನಬಹುದು. ಗಣಕವೊಂದು ತನಗೆ ತಾನೇ ಕಲಿತುಕೊಳ್ಳುವಂತೆ ಅದನ್ನು ಯೋಜಿಸಿರಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟ ಕೆಲಸಬೊಗಸೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ತನ್ನ ಸಾಮರ್ಥ್ಯವನ್ನು ಹೆಚ್ಚಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವ ಥರದಲ್ಲಿ ಅದರ ಸ್ವರೂಪವಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಬೇರುಮಟ್ಟದಲ್ಲಿ ಅದನ್ನು ನೋಡಿದರೆ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಎನ್ನುವುದು ದೊಡ್ಡ ದತ್ತಾಂಶಗಳು ಘ್ಕಿ(daಠಿa) ಗಳ ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಣೆಯಾಗಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಮಾಹಿತಿಯನ್ನು ತಾನೇ ತಾನಾಗಿ ತೆಗೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ನಿರ್ಣಯಗಳನ್ನು ರೂಪಿಸುವುದಕ್ಕೆ ಅದನ್ನು ಬಳಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದೇ ಆಗಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ನಿಮ್ಮ ಭವಿಷ್ಯವಾಣಿ, ಮುಂದಾಗಲಿರುವುದರ ಕುರಿತ ಕಥನಗಳು ಸರಿ ಇರಬಹುದು ತಪ್ಪೇ ಇರಬಹುದು ಅದನ್ನು ಗ್ರಹಿಸಲು ಮತ್ತು ನಿಖರವಾಗಿ ಪ್ರಿಡಿಕ್ಟ್ ಮಾಡಲು ಕಲಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. ಗೂಗಲ್, ಅಮೆಜಾನ್, ನೆಟ್ಫ್ಲಿಕ್ಸ್, ಫ್ಲಿಪ್ಕಾರ್ಟ್, ಮೈಂತ್ರಾ ದಂಥ ಆನ್ಲೈನ್ ವ್ಯಾಪಾರಿ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳು ಗಣಕದಲ್ಲಿ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಹುಡುಕಾಟ, ತಡಕಾಟ, ಖರೀದಿ, ಅದರ ಚರಿತ್ರೆಯ ಅಂಕಿ ಅಂಶ ಮತ್ತು ದಾಖಲೆಗಳನ್ನಿಟ್ಟುಕೊಂಡು ನಿಮಗೆ ಏನು ಇಷ್ಟ ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಊಹೆ ಮಾಡುತ್ತವೆ. ನಿಮ್ಮ ಅಭಿರುಚಿ, ಜೇಬಿನ ಸಾಮರ್ಥ್ಯ ಎಲ್ಲವನ್ನೂ ಅಳೆದು ತೂಗಿ ಇಂಥದ್ದೇ ಕೆಲ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳಿಗೆ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಖರೀದಿ ಚಹರೆಯನ್ನು ರವಾನಿಸುತ್ತವೆ. ಪ್ರತಿನಿತ್ಯ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಇನ್ಬಾಕ್ಸ್ಗೆ ಬಂದು ಬೀಳುವ ವಸ್ತು ಸಾಮಗ್ರಿ, ನಾನಾ ಥರದ ಸೇವೆಗಳ ಸೇವಾದಾತರ ವಿವರಗಳು ಹೇಗೆ ಬಂದಿರುತ್ತವೆ ಎಂದರೆ ಅದೆಲ್ಲವೂ ನೀವು ಜಾಲಾಡಿದ್ದರ ಫಲ (ಕರ್ಮಫಲವೂ ಇರಬಹುದು). ನಿಮ್ಮ ಮೌಸ್ನ ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಂದು ಚಲನೆ, ನಿಲುಗಡೆಯ ಮೇಲೆ ಹದ್ದಿನ ಕಣ್ಣಿರುತ್ತದೆ.
ನಿಮಗೆ ನೆನಪಿರಲಿ, 2018ರಲ್ಲಿ ಇಂಟರ್ನೆಟ್ ಬಳಸಿ ಶೋಧಾಕಾರ್ಯಚರಣೆ ಮಾಡುವವರ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆ 400 ಕೋಟಿ. ಪ್ರತಿ ಸೆಕೆಂಡ್ಗೆ ಏನಿಲ್ಲವೆಂದರೂ 40 ಸಾವಿರ ಸರ್ಚ್ಗಳ ಸಂಸ್ಕರಣೆ ನಡೆಯುತ್ತಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ದಿನವೊಂದಕ್ಕೆ 350 ಕೋಟಿ. ವರ್ಷಕ್ಕೆ 1.2 ಲಕ್ಷ ಕೋಟಿ. ಪ್ರತಿವರ್ಷ ಮನುಷ್ಯ ಸಂಕುಲ ಆನ್ಲೈನ್ನಲ್ಲಿ ವ್ಯಯಿಸುವ ಕಾಲವನ್ನು ಒಟ್ಟು ಮಾಡಿದರೆ ಒಂದು ಶತಕೋಟಿ ವರ್ಷವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ! ಇದರ ಅರ್ಥ ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬರ ಹುಡುಕಾಟದ ಜಾಡು ಹಿಡಿದು ಅವರು ಹೀಗೆ ಎಂದು ಕಣಿ ಹೇಳುವುದಕ್ಕೆ ಎಷ್ಟೊಂದು ಕಷ್ಟ ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಊಹೆ ಮಾಡಿ. ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಒತ್ತಾಸೆಯಿಂದ ಈ ಅಗಾಧ ದತ್ತಾಂಶಗಳನ್ನು ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಿಸಬಹುದು. ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ನ ಬಳಕೆ ಮತ್ತು ಅನ್ವಯದ ಸಾಧ್ಯತೆಗಳು ಹೆಚ್ಚುತ್ತಲೇ ಸಾಗುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಮನುಷ್ಯ ಶ್ರಮದ ಯಾಂತ್ರೀಕರಣ, ಸಂಪರ್ಕ ವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆಯ ನವೀಕರಣ, ನಿತ್ಯದ ಕೆಲಸಗಳಲ್ಲ್ಲಿ ಇದರ ಪಾತ್ರ ಅಗಾಧವಾಗಿದೆ. ಇದನ್ನು ಪವಾಡ ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯುವವರು ಎಷ್ಟು ಮಂದಿ ಇದ್ದಾರೋ ಇದನ್ನೊಂದು ಪ್ರಳಯಸ್ವರೂಪಿ, ಗಂಡಾಂತರಕಾರಿ ಎನ್ನುವವರು ಅಷ್ಟೇ ಮಂದಿ ಇದ್ದಾರೆ. ನಿರ್ದಿಷ್ಟ ವಲಯಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಪ್ರಭಾವವನ್ನು ತಿಳಿದರೆ ಇದರ ಕುರಿತು ಅಂದಾಜು ಸಿಗುತ್ತದೆ.
ಶಿಕ್ಷ ಕರಿಗೆ ನೆರವು
ಶಿಕ್ಷ ಕರಿಗೆ ತರಬೇತಿದಾರ, ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಕ, ಸಮಾಲೋಚಕ, ಮಾರ್ಗದರ್ಶಕ, ತೀರ್ಪುಗಾರ- ಇತ್ಯಾದಿ ಕೆಲಸಗಳ ಕೋಡುಂಟು. ಸದ್ಯಕ್ಕೆ ಯಾವ ಗಣಕ, ರೊಬಾಟ್ ಕೂಟ ಈ ಕಾರ್ಯಗಳಿಗೆ ಸರಿಸಾಟಿಯಾಗಿಲ್ಲ. ಆದರೆ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಮೂಲಕ ಇವುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಕೆಲವೊಂದು ಕಾರ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತ(ಆಟೋಮೇಟೆಡ್)ಗೊಳಿಸಬಹುದು. ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಯೊಬ್ಬರ ಕಲಿಕಾ ಯೋಜನೆಯನ್ನು ಇಂಥದ್ದೇ ಎಂದು ನಿರ್ಧರಿಸುವ ರೀತಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಗಣಕವನ್ನು ರೂಪಿಸಬಹುದು. ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಯ ಅಗತ್ಯವನ್ನು ಕಂಡುಕೊಳ್ಳಬಹುದು. ಗಣಕದ ಕ್ರಮಾವಳಿ (Algorithm) ಯಿಂದ ಪರೀಕ್ಷೆಗಳ ಫಲಿತಾಂಶವನ್ನು ವಿಶ್ಲೇಷಣೆಗೆ ಒಳಪಡಿಸಬಹುದು. ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಯೊಬ್ಬನ ಹಾಜರಿ ಮತ್ತು ಆತನ ಶೈಕ್ಷ ಣಿಕ ಸಾಧನೆಯ ಚರಿತ್ರೆಯ ವಿವರಗಳ ಮೂಲಕ ಆತನ ಜ್ಞಾನದ ಕೊರತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ನ್ಯೂನತೆಗಳನ್ನು ಕಂಡು ಹಿಡಿಯಬಹುದು. ಇದರಿಂದ ತರಗತಿ ಕೋಣೆ ಶಿಕ್ಷಕ ರಹಿತವೇನೂ ಆಗದು. ಆದರೆ ಬೋಧನೆ ಮತ್ತು ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ಪರಿಸರವನ್ನು ಖಂಡಿತ ಸುಧಾರಿಸಬಹುದು. ಶಿಕ್ಷ ಕ ಮತ್ತು ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳ ಹೊರೆಯನ್ನು ಹಗುರಗೊಳಿಸಬಹುದು.
ಕಾನೂನು ತಜ್ಞರ ಕೆಲಸಗಳ ಒತ್ತುವರಿ
ಕಾನೂನು ಮತ್ತು ನ್ಯಾಯಿಕ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ಅನ್ನು ಅವಲಂಬಿಸುತ್ತಿವೆ. ಅದರಲ್ಲೂ ದತ್ತಾಂಶ ಆಧಾರಿತ ಪ್ರಕರಣಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಅನಿವಾರ್ಯತೆಯನ್ನು ಕಂಡುಕೊಂಡಿವೆ. ಅಮೆರಿಕದ ಭಾರಿ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆ ಜೆ.ಪಿ.ಮೊರ್ಗನ್, ಕಂಟ್ರೋಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್ (ಕಾಯಿನ್) ಎನ್ನುವ ತಂತ್ರಾಂಶವನ್ನು ಬಳಸುತ್ತದೆ. ಇದರ ಮೂಲಕ ಹಿಂದಿನ ಪ್ರಕರಣ ಮತ್ತು ದಾಖಲೆಗಳನ್ನು ಕೇವಲ ಸೆಕೆಂಡ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಪರಾಮರ್ಶೆ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಇದು ಒಂದು ಸೆಕೆಂಡ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಮಾಡುವ ಕೆಲಸ, ಮನುಷ್ಯ ಶ್ರಮ ಉಪಯೋಗಿಸಿ ಮಾಡಿದರೆ 3.60.000 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು ಬೇಕಾಗುತ್ತದೆ! ಇದರಿಂದ ವಕೀಲರೇನು ಕೆಲಸ ಕಳೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ನಿಂದ ಪ್ರಕರಣಗಳನ್ನು ಕ್ಷಿಪ್ರವಾಗಿ ಅರ್ಥಮಾಡಿಕೊಳ್ಳಬಹುದು, ಅವುಗಳನ್ನು ತ್ವರಿತವಾಗಿ ವಿಲೇವಾರಿ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಲಕ್ಷಾಂತರ ಪ್ರಕರಣಗಳು ಧೂಳು ತಿನ್ನುತ್ತಿರುವ ನಮ್ಮ ನ್ಯಾಯವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಇಂಥ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನದ ಅಳವಡಿಕೆಯ ಖಂಡಿತ ಇದ್ದೇ ಇದೆ. ಇದರಿಂದ ಆಗುವ ಸಾಮಾಜಿಕ, ಆರ್ಥಿಕ ಪರಿಣಾಮಗಳು ಅಗಾಧ. ನಮ್ಮ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯಗಳು ಈ ಹಾದಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಸಾಗುವ ಅನಿವಾರ್ಯತೆ ಇದ್ದೇ ಇದೆ.
ಕುಶಲ ಮತ್ತು ಶ್ರಮಾಧಾರಿತ ವಲಯ
ಆಸೀಸ್ನ ಗಣಿಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತ ಟ್ರಕ್ಗಳು ಈಗಾಗಲೇ ಕಾರ್ಯನಿರತವಾಗಿವೆ. ಅಪಾಯದ ಸಾಧ್ಯತೆಗಳಿರುವ ವಲಯಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ತೀವ್ರಗತಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಯಾಂತ್ರೀಕರಣವಾಗುತ್ತಿರುವುದು ಎಲ್ಲರಿಗೂ ಗೊತ್ತೇ ಇದೆ. ತಾಲೂಕು ಕಚೇರಿಗಳಲ್ಲಿ, ಬ್ಯಾಂಕುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ, ಸೂಪರ್ ಮಾರ್ಕೆಟ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸ್ವಯಂಚಲಿ ಕಿಯೋಸ್ಕ್ಗಳು ಕಾಣಿಸುತ್ತಿವೆ. ಇವು ಏಷ್ಟೇ ಇರಲಿ, ಬರಲಿ ಮನುಷ್ಯನ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಗೆ ಸಾಟಿಯಲ್ಲ ನಿಜ. ಆದರೆ ಹಾಗೆಂದು ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನದ ಬಳಕೆಯ ವೇಗ ತಗ್ಗಿಲ್ಲ.
ಆರೋಗ್ಯ ರಕ್ಷಕ
ನಿತ್ಯದ ಆರೋಗ್ಯ, ಯೋಗಕ್ಷೇಮದ ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ದೊಡ್ಡ ಪಾತ್ರ ವಹಿಸುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಈಗಾಗಲೇ ರೋಗಿಗಳ ರೋಗವನ್ನು ಕ್ಷಿಪ್ರವಾಗಿ ಪತ್ತೆ ಮಾಡುವುದರಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನವನ್ನು ಬಳಸಲಾಗುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಇದರಿಂದ ಸಮಯ, ಹಣ ಉಳಿತಾಯವಷ್ಟೇ ಅಲ್ಲ ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸೆಯ ಮಟ್ಟವನ್ನು ಎತ್ತರಿಸಬಹುದು. ನಿಮ್ಮ ವಯಸ್ಸು, ಊಟ ತಿಂಡಿ ಪ್ರವೃತ್ತಿ, ಕೆಲಸದ ರೀತಿ ನೀತಿ, ವಂಶವಾಹಿ ಇತಿಹಾಸ- ಈ ಮಾಹಿತಿಗಳನ್ನು ಕಲೆ ಹಾಕಿ ನಿಮಗೆ ಸಂಭವನೀಯ ಆರೋಗ್ಯ ರಿಸ್ಕ್ಗಳು ಏನು ಬರಬಹುದು ಎಂದು ಗಣಕ ನಿಮಗೆ ಹೇಳಬಹುದು. ವಿವಿಧ ಬಗೆಯ ಕ್ಯಾನ್ಸರ್ ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಅದ್ಭುತ ಪಾತ್ರ ವಹಿಸುತ್ತಿದೆ.
2020ಕ್ಕೆ ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತ ನೌಕೆ
ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಮತ್ತು ಎಐ ಮುಂದಿನ ದಿನಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸಾರಿಗೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಕ್ರಾಂತಿಯನ್ನೇ ಉಂಟುಮಾಡಲಿದೆ. ನೌಕಾಯಾನ ಮತ್ತು ರೈಲ್ವೆ ಸಂಪರ್ಕ ಜಾಲದ ನಿಯಂತ್ರಣ ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣವಾಗಿ ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತವಾಗಲಿದೆ. ಸಾರ್ವಜನಿಕ ಸಾರಿಗೆ ಬಸ್ಗಳು ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತವಾಗಿ ಓಡಲು ಸಾಧ್ಯವೇ? ಈ ನಿಟ್ಟಿನಲ್ಲಿ ಚೀನಾ ದೃಢವಾಗಿ ಮುಂದುವರಿದಿದೆ. ರೋಲ್ಸ್ರಾಯ್, ಗೂಗಲ್ ಒಟ್ಟಿಗೆ ಸೇರಿ 2020ರ ವೇಳೆಗೆ ಚಾಲಕ ರಹಿತ ನೌಕೆಯನ್ನು ಅಭಿವೃದ್ಧಿ ಪಡಿಸಲಿವೆ. ಈ ನೌಕೆಯು ಗೂಗಲ್ ಕ್ಲೌಡ್ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ಲರ್ನಿಂಗ್ ಅನ್ನುಬಳಸಿ, ಸಮುದ್ರದಲ್ಲಿರುವ ವಸ್ತುಗಳನ್ನು ಕಂಡುಹಿಡಿಯಲು ದಾರಿ ಗುರುತಿಸಲು ಎಂಜಿನ್ಗೆ ನೆರವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಕೆಲವು ಕೆನಡಾದ ವಾಯುಯಾನ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳು ಪೈಲಟ್ ರಹಿತ ವಿಮಾನಗಳನ್ನು ಅಭಿವೃದ್ಧಿಪಡಿಸಲು ಸಾಕಷ್ಟು ಬಂಡವಾಳ ಹೂಡಿವೆ.
ನಿತ್ಯ ಜೀವನ ಲೀಲೆ
ಗೂಗಲ್ ಹೋಮ್ ಅಸಿಸ್ಟೆಂಟ್ನಂಥ ಯಂತ್ರಗಳು ಈಗಾಗಲೇ ನಮ್ಮ ಮನೆಗಳನ್ನು ಪ್ರವೇಶಿಸಿವೆ. ಕೇವಲ 5-10 ಸಾವಿರ ಬೆಲೆಯ ಚಾಕ್ರಿಯಂತ್ರಗಳು
ಸ್ಮಾರ್ಟ್ ಮನೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಲೈಟ್ ಹಾಕುವ, ಆಫ್ ಮಾಡುವ, ಬಾಗಿಲು ತೆರೆಯುವ ಬಂದ್ ಮಾಡುವ, ವಿವಿಧ ಕೆಲಸಗಳನ್ನು ನಿಮಗೆ ನೆನಪಿಸುವ ಕಾರ್ಯವನ್ನು ಮಾಡುತ್ತಿವೆ. ಫ್ರಿಡ್ಜ್, ವಾಷಿಂಗ್ಮೆಷಿನ್ಗಳನ್ನು ಎಲ್ಲೋ ದೂರದಿಂದಲೇ ಕಂಟ್ರೋಲ್ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಅದರೊಳಗೆ ಏನಿದೆ ಏನಿಲ್ಲ ಎಂದು ಇಣುಕಬಹುದು. ನೀವಿದ್ದಲ್ಲೇ ಅಂಗಡಿಯಾತನಿಗೆ ಆರ್ಡರ್ ಮಾಡಿ ಯಾರೂ ಇಲ್ಲದ ಮನೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಆ ಸರಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಇಳಿಸಿಕೊಂಡು ಅಂಗಡಿಯಾತನಿಗೆ ಟಾಟಾ ಹೇಳಬಹುದು. ಇದು ಭೂತ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆಯಲ್ಲ; ಯಂತ್ರ ಚೇಷ್ಟೆ.
ನಿಮ್ಮ ಭವಿಷ್ಯವನ್ನು ತಿಳಿಸುವ "ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ" ಬಗ್ಗೆ ನಿಮಗೆಷ್ಟು ಗೊತ್ತು?
Source:https://kannada.gizbot.com/scitech/a-brief-history-artificial-intelligence-ai/articlecontent-pf85804-015101.html
ಮಾನವನ ಬುದ್ಧಿಶಕ್ತಿಯಿಂದಲೇ ಜನ್ಮತಾಳಿದ ಈ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ (ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಷಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್) ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನ ಈಗ ಮಾನವನಿಗೇ ಸವಾಲೆಸೆಯುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಮುಂದಿನ 15 ವರ್ಷಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಇದು ಮನುಷ್ಯನ ಬುದ್ಧಿಶಕ್ತಿ ಸಾಮರ್ಥ್ಯವನ್ನು ಮೀರಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. ಇನ್ನು 100 ವರ್ಷಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ವಿಶ್ವದ ಒಟ್ಟಾರೆ ಜನರ ಬುದ್ಧಿಶಕ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಒಟ್ಟುಗೂಡಿಸಿದರೂ ಇದಕ್ಕೆ ಸರಿಸಾಟಿಯಾಗಲಾರದು ಎಂದು ತಜ್ಞರು ಎಚ್ಚರಿಸುತ್ತಿದ್ದಾರೆ.!! ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನವನ್ನು ಸರಳವಾಗಿ ಹೇಳುವುದಾದರೆ ಇದು ಕೇವಲ ಒಂದು ಕಂಪ್ಯೂಟರ್ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮ್. ಆದರೆ, ಇದು ಇಷ್ಟಕ್ಕೇ ಸೀಮಿತವಾಗಿದ್ದರೆ ಇದರ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಚರ್ಚಿಸುವ ಅವಶ್ಯಕತೆ ಇರುತ್ತಿರಲಿಲ್ಲ. ಆದರೆ, ಇದು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಕಂಪ್ಯೂಟರ್ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮ್ ಅಲ್ಲ. ಪರಿಸ್ಥಿತಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಅನುಗುಣವಾಗಿ ತಾನೇ ನಿರ್ಣಯಗಳನ್ನು ತೆಗೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವಪ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮ್!! ಹಾಗಾದರೆ, ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಇತಿಹಾಸ ಏನು? ಸಾಧಕ ಬಾಧಕಗಳೇನು ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಸ್ಲೈಡರ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ತಿಳಿಯಿರಿ.!!

'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ಹುಟ್ಟಿದ್ದು ಯಾವಾಗ? ಇತ್ತೀಚಿಗೆ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಪ್ರಾಮುಖ್ಯತೆ ಪಡೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತಿರುವ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ (ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್) 1956ರಿಂದಲೇ ಬಳಕೆಗೆ ಬಂದಿದೆ. ಎಲ್ಐಎಸ್ಪಿ ಎನ್ನುವ ಪ್ರೊಗ್ರಾಮಿಂಗ್ ಲಾಂಗ್ವೇಜ್ ಅಭಿವೃದ್ಧಿಪಡಿಸಿದ ಜಾನ್ ಮೆಕ್ಕಾರ್ತಿ ಎನ್ನುವ ವಿಜ್ಞಾನಿ ಇದಕ್ಕೆ ‘ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ಎಂಬ ಹೆಸರನ್ನು ಸೂಚಿಸಿದರು.!!
ಪ್ರಚಲಿತವಾಗಿದ್ದು ಚೆಸ್ನಿಂದ!! ಮಾನವನನ್ನು ಬಿಟ್ಟರೆ ಇತರರಿಂದ ಚೆಸ್ ಆಡಲು ಸಾಧ್ಯವೇ ಇಲ್ಲ ಎನ್ನುವ ಕಾಲದಲ್ಲಿ ಐಬಿಎಂನ ‘ಡೀಪ್ ಬ್ಲೂ' ಸೂಪರ್ ಕಂಪ್ಯೂಟರ್ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನದಿಂದ ವಿಶ್ವ ಚೆಸ್ ಚಾಂಪಿಯನ್ ಆಗಿದ್ದ ಗ್ಯಾರಿ ಕಾಸ್ಪೆರೆಸೊ ಅವರನ್ನು ಸೋಲಿಸಿತು. ಈ ಘಟನೆ ನಂತರ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಯ ಶಕ್ತಿ ಏನೆಂಬುದು ವಿಶ್ವಕ್ಕೆ ತಿಳಿಯಿತು.!!

ನಮಗೆ ಅರಿವಿಲ್ಲದಂತೆಯೇ ಹಾಸುಹೊಕ್ಕಾಗಿದೆ.!! ನಮ್ಮ ಆಲೋಚನೆಗಳನ್ನು ಗ್ರಹಿಸಿ ಅದಕ್ಕೆ ಅನುಗುಣವಾದ ಕೆಲಸಗಳನ್ನು ಮಾಡುತ್ತಿರುವ ಇವೆಲ್ಲಾ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಯ ರೂಪಗಳೇ. ಹೀಗೆ ನಮಗೆ ಅರಿವಿಲ್ಲದಂತೆ ಇದು ನಮ್ಮ ಜೀವನಕ್ಕೆ ಕಾಲಿಟ್ಟಿದೆ. ಯಾವುದಾದರೂ ಮಾಹಿತಿಗಾಗಿ ಗೂಗಲ್ನಲ್ಲಿ ಎರಡು ಅಕ್ಷರಗಳನ್ನು ಟೈಪ್ ಮಾಡುತ್ತಿದ್ದಂತೇ ನಾವು ಏನು ಹುಡುಕಲು ಪ್ರಯತ್ನಿಸುತ್ತಿದ್ದೇವೆ ಎಂದು ಊಹಿಸಿಸುವುದು ಇದರಿಂದಲೇ.!!

'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ವಿಶೇಷವೇನು? ವೈದ್ಯ, ವಿಜ್ಞಾನ, ವಾಣಿಜ್ಯ, ಸೇನೆ, ಸೇವೆ ಹೀಗೆ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರಗಳಲ್ಲೂ ಇದರದ್ದೇ ಮೇಲುಗೈ.!! ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತ ವಾಹನ, ಯಂತ್ರಗಳು, ಚಾಟ್ಬೋಟ್ಸ್, ಪರ್ಸನಲ್ ಡಿಜಿಟಲ್ ಅಸಿಸ್ಟಂಟ್ ಎಲ್ಲವೂ ಕೂಡ 'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ವಿಶೇಷತೆಗಳೆ.! ಸ್ವಯಂ ಆಗಿ ಕಲಿಯುವ ಯಂತ್ರಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಕೆಲಸ ನಿರ್ವಹಿಸಲಿದ್ದು, ಪರಿಸ್ಥಿತಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಅನುಗುಣವಾಗಿ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮಿಂಗ್ ಮಾಡಿಕೊಂಡು ಅದರ ಅಧಾರವಾಗಿ ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್ ಕೆಲಸ ಮಾಡುತ್ತದೆ!

'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ಪರಿಣಾಮಗಳೇನು? ಮಾನವನ ಕೆಲಸ ಮತ್ತು ಜೀವನವನ್ನೇ ಬಹಳ ಸುಲಭಗೊಳಿಸುವ ಈ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಮಾನವನ ಒಳಿತಿಗೆ ಕಾರಣವಾಗಬಲ್ಲದು.! ಆದರೆ, ಇದೇ ವಿಜೃಂಭಿಸಿದರೆ ಹಲವರು ಉದ್ಯೋಗ ಕಳೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವ ಸಾಧ್ಯತೆ ಇದೆ ಎಂದು ತಜ್ಞರು ಹೇಳುತ್ತಿದ್ದಾರೆ.! ಭಯೋತ್ಪಾದಕರು, ಕಳ್ಳರು ದುರುದ್ದೇಶಗಳಿಗೆ ಇದರ ಶಕ್ತಿಯಿಂದ ಕೆಲಸ ಮಾಡುವ ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತ ಯಂತ್ರಗಳು ಸಿಕ್ಕರೆ ಆಗಬಹುದಾದ ಪರಿಣಾಮಗಳನ್ನು ಸಹ ಯೋಚಿಸಬೇಕಿದೆ.!!
ಮಾನವನ ಬುದ್ಧಿಶಕ್ತಿಯಿಂದಲೇ ಜನ್ಮತಾಳಿದ ಈ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ (ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಷಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್) ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನ ಈಗ ಮಾನವನಿಗೇ ಸವಾಲೆಸೆಯುತ್ತಿದೆ. ಮುಂದಿನ 15 ವರ್ಷಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಇದು ಮನುಷ್ಯನ ಬುದ್ಧಿಶಕ್ತಿ ಸಾಮರ್ಥ್ಯವನ್ನು ಮೀರಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. ಇನ್ನು 100 ವರ್ಷಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ವಿಶ್ವದ ಒಟ್ಟಾರೆ ಜನರ ಬುದ್ಧಿಶಕ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಒಟ್ಟುಗೂಡಿಸಿದರೂ ಇದಕ್ಕೆ ಸರಿಸಾಟಿಯಾಗಲಾರದು ಎಂದು ತಜ್ಞರು ಎಚ್ಚರಿಸುತ್ತಿದ್ದಾರೆ.!! ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನವನ್ನು ಸರಳವಾಗಿ ಹೇಳುವುದಾದರೆ ಇದು ಕೇವಲ ಒಂದು ಕಂಪ್ಯೂಟರ್ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮ್. ಆದರೆ, ಇದು ಇಷ್ಟಕ್ಕೇ ಸೀಮಿತವಾಗಿದ್ದರೆ ಇದರ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಚರ್ಚಿಸುವ ಅವಶ್ಯಕತೆ ಇರುತ್ತಿರಲಿಲ್ಲ. ಆದರೆ, ಇದು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಕಂಪ್ಯೂಟರ್ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮ್ ಅಲ್ಲ. ಪರಿಸ್ಥಿತಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಅನುಗುಣವಾಗಿ ತಾನೇ ನಿರ್ಣಯಗಳನ್ನು ತೆಗೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವಪ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮ್!! ಹಾಗಾದರೆ, ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಇತಿಹಾಸ ಏನು? ಸಾಧಕ ಬಾಧಕಗಳೇನು ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಸ್ಲೈಡರ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ತಿಳಿಯಿರಿ.!!

'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ಹುಟ್ಟಿದ್ದು ಯಾವಾಗ? ಇತ್ತೀಚಿಗೆ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಪ್ರಾಮುಖ್ಯತೆ ಪಡೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತಿರುವ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ (ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್) 1956ರಿಂದಲೇ ಬಳಕೆಗೆ ಬಂದಿದೆ. ಎಲ್ಐಎಸ್ಪಿ ಎನ್ನುವ ಪ್ರೊಗ್ರಾಮಿಂಗ್ ಲಾಂಗ್ವೇಜ್ ಅಭಿವೃದ್ಧಿಪಡಿಸಿದ ಜಾನ್ ಮೆಕ್ಕಾರ್ತಿ ಎನ್ನುವ ವಿಜ್ಞಾನಿ ಇದಕ್ಕೆ ‘ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ಎಂಬ ಹೆಸರನ್ನು ಸೂಚಿಸಿದರು.!!

ಪ್ರಚಲಿತವಾಗಿದ್ದು ಚೆಸ್ನಿಂದ!! ಮಾನವನನ್ನು ಬಿಟ್ಟರೆ ಇತರರಿಂದ ಚೆಸ್ ಆಡಲು ಸಾಧ್ಯವೇ ಇಲ್ಲ ಎನ್ನುವ ಕಾಲದಲ್ಲಿ ಐಬಿಎಂನ ‘ಡೀಪ್ ಬ್ಲೂ' ಸೂಪರ್ ಕಂಪ್ಯೂಟರ್ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನದಿಂದ ವಿಶ್ವ ಚೆಸ್ ಚಾಂಪಿಯನ್ ಆಗಿದ್ದ ಗ್ಯಾರಿ ಕಾಸ್ಪೆರೆಸೊ ಅವರನ್ನು ಸೋಲಿಸಿತು. ಈ ಘಟನೆ ನಂತರ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಯ ಶಕ್ತಿ ಏನೆಂಬುದು ವಿಶ್ವಕ್ಕೆ ತಿಳಿಯಿತು.!!

ನಮಗೆ ಅರಿವಿಲ್ಲದಂತೆಯೇ ಹಾಸುಹೊಕ್ಕಾಗಿದೆ.!! ನಮ್ಮ ಆಲೋಚನೆಗಳನ್ನು ಗ್ರಹಿಸಿ ಅದಕ್ಕೆ ಅನುಗುಣವಾದ ಕೆಲಸಗಳನ್ನು ಮಾಡುತ್ತಿರುವ ಇವೆಲ್ಲಾ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆಯ ರೂಪಗಳೇ. ಹೀಗೆ ನಮಗೆ ಅರಿವಿಲ್ಲದಂತೆ ಇದು ನಮ್ಮ ಜೀವನಕ್ಕೆ ಕಾಲಿಟ್ಟಿದೆ. ಯಾವುದಾದರೂ ಮಾಹಿತಿಗಾಗಿ ಗೂಗಲ್ನಲ್ಲಿ ಎರಡು ಅಕ್ಷರಗಳನ್ನು ಟೈಪ್ ಮಾಡುತ್ತಿದ್ದಂತೇ ನಾವು ಏನು ಹುಡುಕಲು ಪ್ರಯತ್ನಿಸುತ್ತಿದ್ದೇವೆ ಎಂದು ಊಹಿಸಿಸುವುದು ಇದರಿಂದಲೇ.!!

'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ವಿಶೇಷವೇನು? ವೈದ್ಯ, ವಿಜ್ಞಾನ, ವಾಣಿಜ್ಯ, ಸೇನೆ, ಸೇವೆ ಹೀಗೆ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರಗಳಲ್ಲೂ ಇದರದ್ದೇ ಮೇಲುಗೈ.!! ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತ ವಾಹನ, ಯಂತ್ರಗಳು, ಚಾಟ್ಬೋಟ್ಸ್, ಪರ್ಸನಲ್ ಡಿಜಿಟಲ್ ಅಸಿಸ್ಟಂಟ್ ಎಲ್ಲವೂ ಕೂಡ 'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ವಿಶೇಷತೆಗಳೆ.! ಸ್ವಯಂ ಆಗಿ ಕಲಿಯುವ ಯಂತ್ರಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಕೆಲಸ ನಿರ್ವಹಿಸಲಿದ್ದು, ಪರಿಸ್ಥಿತಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಅನುಗುಣವಾಗಿ ಪ್ರೋಗ್ರಾಮಿಂಗ್ ಮಾಡಿಕೊಂಡು ಅದರ ಅಧಾರವಾಗಿ ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್ ಕೆಲಸ ಮಾಡುತ್ತದೆ!

'ಆರ್ಟಿಫಿಶಿಯಲ್ ಇಂಟಲಿಜೆನ್ಸ್' ಪರಿಣಾಮಗಳೇನು? ಮಾನವನ ಕೆಲಸ ಮತ್ತು ಜೀವನವನ್ನೇ ಬಹಳ ಸುಲಭಗೊಳಿಸುವ ಈ ಕೃತಕ ಬುದ್ಧಿಮತ್ತೆ ಮಾನವನ ಒಳಿತಿಗೆ ಕಾರಣವಾಗಬಲ್ಲದು.! ಆದರೆ, ಇದೇ ವಿಜೃಂಭಿಸಿದರೆ ಹಲವರು ಉದ್ಯೋಗ ಕಳೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳುವ ಸಾಧ್ಯತೆ ಇದೆ ಎಂದು ತಜ್ಞರು ಹೇಳುತ್ತಿದ್ದಾರೆ.! ಭಯೋತ್ಪಾದಕರು, ಕಳ್ಳರು ದುರುದ್ದೇಶಗಳಿಗೆ ಇದರ ಶಕ್ತಿಯಿಂದ ಕೆಲಸ ಮಾಡುವ ಸ್ವಯಂಚಾಲಿತ ಯಂತ್ರಗಳು ಸಿಕ್ಕರೆ ಆಗಬಹುದಾದ ಪರಿಣಾಮಗಳನ್ನು ಸಹ ಯೋಚಿಸಬೇಕಿದೆ.!!
5 Open-Source Machine Learning Frameworks and Tools
Source : https://dzone.com/articles/5-open-source-machine-learning-frameworks-and-tool





The list below describes five of the most popular open-source machine learning frameworks, what they offer, and what use cases they can best be applied to.
Practical machine learning development has advanced at a remarkable pace. This is reflected by not only a rise in actual products based on, or offering, machine learning capabilities but also a rise in new development frameworks and methodologies, most of which are backed by open-source projects.
In fact, developers and researchers beginning a new project can be easily overwhelmed by the choice of frameworks offered out there. These new tools vary considerably — and striking a balance between keeping up with new trends and ensuring project stability and reliability can be hard.
The list below describes five of the most popular open-source machine learning frameworks, what they offer, and what use cases they can best be applied to.
1. TensorFlow

Made public and open-sourced two years ago, TensorFlow is Google's own internal framework for deep learning (artificial neural networks). It allows you to build any kind of neural network (and other computational models) by stacking the typical mathematical operations for NNs in a "computational graph."
The magic happens when the model is trained, and TensorFlow knows how to back-propagate errors through the computational graph, thus learning the correct parameters. TensorFlow is general enough to be used for building any type of network — from text to image classifiers, to more advanced models like generative adversarial neural networks (GANs), and even allows other frameworks to be built on top of it (see Keras and Edward down the list).
True, we could have selected other prominent deep learning frameworks that are equally as effective as TensorFlow-like Theano, Torch, or Caffe — but TensorFlow has risen in popularity so quickly that it's now arguably the de facto industry standard for deep learning (and yes, being developed and used by Google itself does lend it extra kudos.) It also has the most active and diverse ecosystem of developers and tools of all the DL frameworks.
Another consideration is that since deep learning frameworks are evolving on a daily basis and are often buggy, it's important to know that your Stack Overflow search will yield results-and almost every bug and difficulty in TensorFlow is "Stack Overflow solvable."
The main pitfall many users cite against TensorFlow is its intrinsic difficulty of use, due in part to the fact that the framework is so customizable and "down to the metal" of every little detail, almost every computation in the neural network you're building needs to be explicitly programmed into the model. Some may view this as a benefit, but unless you're very familiar with every implementation detail of the model you're trying to build (differences between activation functions, matrix multiplication dimensionality, etc.), TensorFlow may become burdensome. Users who wish to work with more high-level models will enjoy Keras, which is next on our list.
2. Keras

Keras is a high-level interface for deep learning frameworks like Google's TensorFlow, Microsoft's CNTK, Amazon's MXNet, and more. Initially built from scratch by François Chollet in 2015, Keras quickly became the second-fastest growing deep learning framework after TensorFlow. This is easily explained by its declared purpose: to make drafting new DL models as easy as writing new methods in Python. This is why, for anyone who has struggled with building models using TensorFlow at all, Keras is nothing short of revolutionary-it allows you to easily create common types of neuron layers, select metrics, error function, and optimization method, and to train the model quickly and easily.
Its main power lies in its modularity: Almost every neural building block is available in the library (which is regularly updated with new ones), and they can all be easily composed on top of one another, to create more customized and elaborate models.
Some cool recent projects that use Keras are Object Detection and Segmentation by Matterport, and this cool grayscale image colorization model. Uber has also recently revealed in a post that their distributional deep learning framework, Horovod, also supports Keras for fast prototyping.
3. SciKit-Learn

With the recent explosion of deep learning, one may get the impression that other, more "classic" machine learning models are no longer in use. This is far from true — in fact, many common machine learning tasks can be solved using traditional models that were industry standard before the deep learning boom-and with much greater ease. While deep learning models are great at capturing patterns, it's often hard to explain what and how they have learned, an important requirement in many applications (see Lime, below, for model explanations). Plus, they're often very computationally expensive to train and deploy. Also, standard problems like clustering, dimensionality reduction, and feature selection can often be solved more easily using traditional models.
SciKit-learn is an academia-backed framework that has just celebrated its tenth anniversary. It contains almost every machine learning model imaginable — from linear and logistic regressors to SVM classifiers and random forests — and it has a huge toolbox of preprocessing methods like dimensionality reduction, text transformations, and many more.
In our humble opinion, SciKit-learn is truly one of the greatest feats of the Python community, if only for its documentation — some of the best docs we've seen for any Python package. In fact, its user guide is so good that you could use it as a textbook for data science and machine learning. Any start-up about to jump into deep learning waters should first consider opting for a SciKit model that may provide similar performance, while also saving development time.
4. Edward
Edward is one of the most promising and intriguing projects seen in the community in a while.
Created by Dustin Tran, a Ph.D. student at Columbia University and a researcher at Google, alongside a group of AI researchers and contributors, Edward is built on top of TensorFlow and fuses three fields: Bayesian statistics and machine learning, deep learning, and probabilistic programming.
It allows users to construct probabilistic graphical models (PGM). It can be used to build Bayesian neural networks, along with almost every model that can be represented as a graph and uses probabilistic representations. Its uses are still limited more to hardcore AI models than to real-world production, but since PGMs are proving increasingly useful in AI research, we can assume that practical uses will be found for these models in the near future.
Recently, Edward reached another impressive milestone, announcing that it will be officially integrated into the TensorFlow code base.
5. Lime
One of the biggest challenges with machine learning is explaining what your model has learned —in other words, debugging its internal representations. Say you've built a text classifier that works pretty well, but fails embarrassingly for some sentences. For example, you'd like to know which words in the sentence "Apple iPad Pro with red case" caused the model to classify the device as a surfboard instead of a tablet — finding out that the word "red" is more typical to surfboards than to smartphones, leading the model to a mistake. This can be done by inspecting the model's internal weights for each word in its vocabulary, a process that may become cumbersome for more complicated models with a lot of features and weights.
Lime is an easy-to-use Python package that does this for you in a more intelligent way. Taking a constructed model as input, it runs a second "meta" approximator of the learned model, which approximates the behavior of the model for different inputs. The output is an explainer for the model, identifying which parts of any input helped the model reach a decision and which didn't.
It then displays the results in a readable and interpretable way — for example, an explanation for a text classifier would look like this, highlighting the words that helped the model reach a decision, and their respective probabilities:

Image taken from project’s GitHub page
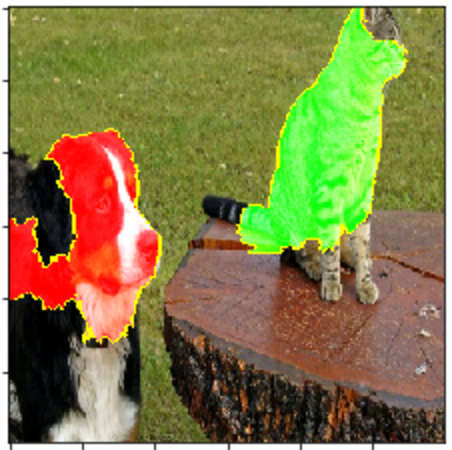
Lime supports — learn models out of the box, as it does for any classifier model that takes in raw text or an array, and outputs a probability for each class. It can also explain image classification models. The following screenshot explains a classifier that learned to distinguish between cats and dogs. In the screenshot, Lime explains which areas in the image were used by the model for classifying the image as "cat" (the green zone), and which areas had a negative weight, causing it to lean toward a "dog" classification.

Image taken from project’s GitHub page
Endnotes
We have listed here three major frameworks and two promising tools for machine learning researchers and engineers to consider when approaching a project, either by building it from scratch or trying to improve it.
As the practical machine learning development world advances, we hope to see more mature frameworks and tools. In a future post, we will list even more advanced and neat tools specially created for machine learning engineers.
Sunday 24 June 2018
Top Competency Skills for Current Job Trends
Current Job Trends:
- Artificial Intelligence Engineer
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Data Scientist and Data Analyst
- Computer Network and Cyber Security Expert
- Block Chain Developer / Bit Coin Miner
- Full Stack (Front to Back End) Developers for Mobile, Web and Desktop Applications.
Top Programming Languages
- Python
- Java Script, Angular JS
- Java
- SQL
- C: Objective C and Embedded C
- PhP
Essential Skills :
1. Programming Skills
2. Mathematics
3. Communication Skills
......Dr.TGS
Thursday 21 June 2018
Blockchain Tutorial – A Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain Technology
The growth of Bitcoin and Blockchain technology has been so rapid, that even those who haven’t heard of cryptocurrency or know about its working, are looking to invest and explore this field. This Blockchain tutorial blog will essentially provide you with all the fundamental knowledge you need regarding Bitcoin and Blockchain in the following sequence:
- Issues with the current Banking System
- How Blockchain solves these issues
- What is Blockchain and Bitcoin
- Features of Blockchain
- Use Case
- Demo: Implementing Digital Banking using Blockchain
https://www.edureka.co/blog/blockchain-tutorial/
What is blockchain? The most disruptive tech in decades.
The distributed ledger technology, better known as blockchain, has the potential to eliminate huge amounts of record-keeping, save money and disrupt IT in ways not seen since the internet arrived.
What is blockchain?
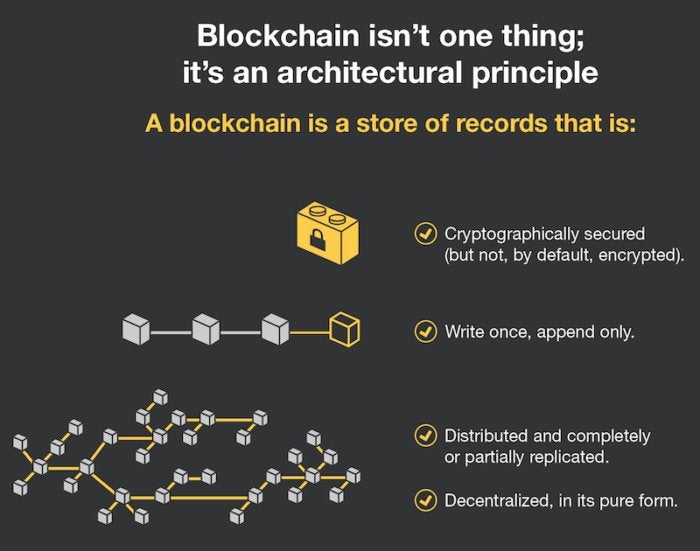
First and foremost, Blockchain is a public electronic ledger that can be openly shared among disparate users and that creates an unchangeable record of their transactions, each one time-stamped and linked to the previous one. Each digital record or transaction in the thread is called a block (hence the name), and it allows either an open or controlled set of users to participate in the electronic ledger. Each block is linked to a specific participant.Blockchain can only be updated by consensus between participants in the system, and when new data is entered, it can never be erased. The blockchain contains a true and verifiable record of each and every transaction ever made in the system.
In layman's terms, blockchain is a write-once, append-many electronic ledger.
Blockchain isn't a single technology. Rather it's an architecture that allows disparate users to make transactions and then creates an unchangeable record of those transactions.
 Forrester Research
Forrester Research In another example, one of the most prevalent blockchain platforms, Ethereum, doesn't support the use of decimal points in its script for smart (self executing) contracts. Those coding a blockchain network would need to create a workaround.
The Linux Foundation has created tools for building out blockchain collaboration networks. And in July, the open-source developer unveiled Hyperledger Fabric 1.0, a collaboration tool for building blockchain distributed ledger business networks, such as smart contracts.
While some industry groups are working toward standardizing versions of blockchain software, there are also about 200 startups working on their own versions of the distributed ledger technology.
Why is blockchain getting so much buzz? In a word, Bitcoin. Bitcoin is the wildly hyped cryptocurrency, a method of transacting payments over an open network using digital bits and encryption. It was the first ever decentralized one when it was created in 2009. Other forms of cryptocurrency or virtual money, such as Ether (based on the Ethereum blockchain application platform), have also sprung up and have opened new venues for cross-border monetary exchanges.
The term bitcoin was first... well, coined in 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto (likely a pseudonym for one or more developers) wrote a paper about a "peer-to-peer version of electronic cash that would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution."
What does blockchain do?
As a peer-to-peer network, combined with a distributed time-stamping server, blockchain ledgers can be managed autonomously to exchange information between disparate parties. There's no need for an administrator. In effect, the blockchain users are the administrator.Additionally, blockchain networks can be used for "smart contracts," or scripts that automatically execute when certain conditions are met. For example, Ethereum Ether exchange users must meet pre-determined conditions that prove someone owns the cryptocurrency and have authority to send the money they claim to own. In addition, multiple blockchain users can create contracts that require more than one set of inputs to trigger a transaction.
One example: real estate transactions require sign offs between buyers, sellers and their financial institutions.
 Network World
Network World How secure is blockchain?
While no system is "unhackable," blockchain's simple topology is the most secure today, according to Alex Tapscott, the CEO and founder of Northwest Passage Ventures, a venture capital firm that invests in blockchain technology companies."In order to move anything of value over any kind of blockchain, the network [of nodes] must first agree that that transaction is valid, which means no single entity can go in and say one way or the other whether or not a transaction happened," Tapscott said. "To hack it, you wouldn't just have to hack one system like in a bank..., you'd have to hack every single computer on that network, which is fighting against you doing that."
The computing resources of most blockchains are tremendous, Tapscott said, because it's not just one computer but many. For example, the Bitcoin blockchain harnesses anywhere between 10 and 100 times as much computing power compared to all of Google's serving farms put together.
 Forrester Research
Forrester Research Public vs. private blockchains
There are a variety of blockchain permutations, and they fall mainly into one of two categories - public or private. Public blockchains allow anyone to see or send transactions as long as they're part of the consensus process. There are also consortium blockchains, where only a pre-selected number of nodes are authorized to use the ledger. For example, a group of banks and their clearinghouse might use blockchain as part of the trade-clearing, where each node is associated with a step in the verification process.Private blockchains, in contrast, restrict the ability to write to a distributed ledger to one organization, such as a group of employees within a corporation, or between a set number of organizations, such as a number of banks that agree to a network partnership.
Along the way, blockchain - because of its self-policing security - eliminates huge amounts of record keeping, which can get very confusing when multiple parties are involved in a transaction, according to Saurabh Gupta, vice president of strategy at IT services company Genpact.
Which industries use blockchain?
Shipping. Fintech. Healthcare, Energy. Blockchains are being put to a wide variety of uses in several industries. (Most recently it's been touted as a way to exchange carbon credits.)In shipping, for example, a bill of lading for cargo shipments has traditionally been paper based, which requires multiple sign-offs by inspectors and receivers before goods can be delivered. Even when the system is electronic, it still requires multiple parties to sign off on cargo shipments, creating a lengthy administrative process. To try and streamline that cumbersome process, the world's largest container shipment operator, Maersk, in March 2017 announced it is using a blockchain-based ledger to manage and track the paper trail of tens of millions of shipping containers by digitizing the supply chain. And Maersk has now teamed up with IBM on a new blockchain-based electronic shipping platform. It’s expected to be up and running later in 2018.
[ Further reading: Blockchain breaks out in the enterprise ]
Each participant in the shipping supply chain can view the progress of goods through the blockchain ledger, understanding where a container is in transit. They can also see the status of customs documents, or view bills of lading and other data in real time. And, because it creates an immutable record, no one party can modify, delete or even append any one of the blocks without the consensus from others on the network.
"Blockchain and distributed ledgers may eventually be the method for integrating the entire commercial world's record keeping," Gupta said.
Genpact, for example, announced a service for finance and accounting that leverages blockchain-based smart contracts to capture all terms and conditions between a customer and an organization for an order.
Blockchain in FinTech
But it's financial services technology where blockchain is currently shining brightly.At a high level, blockchain removes third parties from the transaction equation; in other words, a financial transaction on a blockchain needs no bank or government backer, and that means no fees.
Because blockchain entries can be seen in real time, the technology also has the potential to reduce time for clearance and settlement, which can take up to five days.
Accenture recently released a report claiming blockchain technology could reduce infrastructure costs for eight of the world's 10 largest investment banks by an average of 30%, "translating to $8 billion to $12 billion in annual cost savings for those banks."
In the case of cross-border payments, processing is often complex and includes multiple layers of communication among payment participants to verify transactions - an operation known as payment and settlement.
Payments, clearance and settlement in the financial services industry - including stock markets - is rife with inefficiencies because each organization in the process maintains its own data and must communicate with the others through electronic messaging about where it is in the process. As a result, settlements typically take two days. Those delays in settlements force banks to set aside money that could otherwise be invested.
Because it can instantly share data with each organization involved in a blockchain database or ledger, the technology reduces or eliminates the need for reconciliation, confirmation and trade break analysis. That helps yield a more efficient and effective clearance and settlement process, according to Accenture.
Source :https://www.computerworld.com/article/3191077/security/what-is-blockchain-the-most-disruptive-tech-in-decades.html
Wednesday 20 June 2018
Top Countries Hiring Most Number Of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning Experts
https://analyticsindiamag.com/top-countries-hiring-most-number-of-artificial-intelligence-machine-learning-experts/


Demand for artificial intelligence and machine learning experts is on the rise globally despite a fear that AI will eat away at many jobs. The rate at which global companies are hiring gives us a different picture. The technological advancement is still creating more positions as companies need high-skilled AI talents to develop and maintain a wide range of applications. According to Indeed, employers demand for AI talents has more than doubled over the past three years and the number of job postings as a share of all job postings have increased by 119 percent. The top 10 jobs in demand right now are:
- Data Scientist
- Software Engineer
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Software Architect
- Data Analyst
- Data Warehouse Engineer
- Full Stack Developers
- Research Scientist
- Front End Developer
- Product Manager
AI and machine learning has also strongly gaining ground in India, which is one of the top 15 countries in terms of talent, corporates who use ML, and authors who write about it. Cheaper cost of set up and availability of talent has made India a favourite place for tech giants such as Microsoft, Google and IBM to set up shop.
Here’s let’s take a look at the countries that are increasingly hiring more AI talents:
United States
US has been the leader in attracting AI and machine learning talent. A study by Pysa shows that the top 20 AI companies are spending more than $650 million to hire AI talent and that there are more than 10,000 positions available at top employers across the country. The total annual investment among the 20 employers that are looking to hire AI talents is $33,292,647, which indicates that the future success of the companies heavily depends on AI technologies and the talent to create them.
According to Glassdoor and Pysa, the top recruiters in US are Amazon, Google, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Facebook, Intel, Rocket Fuel, General Electric, Cylance, Oculus VR, Booz Allen Hamilton, Huawei, Adobe, Accenture, iRobot, Magic Leap, Rethink Robotics, BAE Systems, HERE, IBM, Samsung, Lenovo, MoTek Technologies, Uber, PCO innovation, Rakuten Marketing, and Wells Fargo. However, none of the reports listed Apple among the top recruiter. The Cupertino-based company comes way down at 96 on the list. This low ranking may be because of the company’s affinity for secrecy which is hurting the iPhone maker in the race to hire AI talent.
Recruiters in the US are seeking tech and engineering talents with deep learning, machine learning, AI, neural networks, computer vision and reinforcement skills. Additionally, the country is estimated to have 2,50,000 open data science jobs by 2024.
Canada
After the US, Canada is gradually becoming a go-to place for AI experts. According to an Indeed report, jobs in Canada requiring AI skills have grown by 1,069 percent since 2013 — a growth rate faster than the UK and US. Companies that are actively hiring for AI skills in Canada are — Royal Bank of Canada, IBM, Scotiabank, KPMG, Amazon, LoyaltyOne, TD Bank, Kinaxis, Huawei and Capital One, among others. Universities across the country are allowing researchers and scientist to lay the groundwork for a breakthrough in AI. The Justin Trudeau-led government invested dramatically in AI research in the past year. Last year, Canada released its national strategy with a plan to invest $125 million in a Pan-Canadian AI Strategy that is focused on increasing the number of researchers and skilled graduates.
Additionally, global tech companies such as DeepMind, Microsoft, Facebook and Google among others are also setting up their research labs in the country and tapping Canadian talents to head new AI arms.
Europe
According to reports, AI-related jobs have tripled over the last three years. The two most sought-after positions by employers are data scientist and machine learning engineers. In the UK, AI jobs pay well above the average salary, data scientist take home £56,385 a year and ML engineers earning an average of £54,617 a year. However, research suggests that the number of AI jobs available in Britain was six times higher than the number of interested candidates.
On the other hand, the number of job opportunities is little less in Germany. “When it comes to machinery, Germany has a strong presence of young professionals and academics which has remained sort of hidden and is not always exploited well,” said Yasser Jadidi, head of AI research at the Bosch Center for AI. However, now the company has been thinking to commercialise AI expertise for business. Other European countries like France and Spain too have a significant number of AI experts. In last one year at least 20 development centers have been set up in the countries like Poland, Romania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Austria and Ireland. Nearly 200,000students graduate in engineering and sciences every year from Universities in Central and Eastern European countries.
China
Beijing is investing a gargantuan sum of money to make the country No.1 in the application of artificial intelligence. The country is hiring tens and thousands of people to shore up cybersecurity, help censor online content. The salaries that are paid to the top AI talents are within striking distance of those offered in the US.
Out of China’s top 10 employers in AI, half are American, claims LinkedIn’s report. The top US tech companies in China hiring AI talents are Intel, IBM and Microsoft. Alibaba, Baidu, Huawei, and Tencent, are among the top Chinese employers in the country. However, China still lags behind in terms of AI position, which has about 50,000 AI position. On the other hand, US has about 80,000 AI position.
According to a tech recruitment website, the salaries of the top graduates working on AI range from 300,000 yuan ($47,066) to 600,000 yuan ($94,132) an annum. While the salaries of team leaders with three-to-five years of experience can make more than 1.5 million yuan ($23,533,100) annually. Most of the jobs are in Beijing or Shenzhen. The tech firms are also actively recruiting Chinese students from US college. The job creation is a part of governments drive to become AI superpower and move the Chinese economy up the value chain with emphasis on areas like IT, robotics and energy-saving vehicles.
Japan
After becoming a world leader in electronics, the country is now focused on building its robotics industry. Foreign software engineers and other information technology specialists are increasingly joining Japan’s robotic startups. Start Today Co, which operates popular online fashion shopping website Zozotown is also hiring tech workers in fields ranging from AI to cryptography and offering annual salaries of as much as 100 million yen ($944,000). The country has roughly 117 active researchers presenting at Neural Information Processing Systems and other leading conferences.
India
India too is not far behind other countries in terms AI1 hiring, the country is expected to see a 60 per cent rise by this year due to increasing adoption of automation. The presence of multi-billion dollar IT companies, global software product companies with their research and development bases in India and venture capital industry focused on AI and machine learning has given rise to a talent pool. Further, as India is heading towards Digital India, the IT industry will require 50 percent more workforce equipped with digital skills. “The growing opportunities in the digital technology arena including government initiative like Digital India will add jobs in digital technologies, AI, robotics. The IT industry is expected to add around 1.8-2 lakh jobs this year,” said Alka Dhingra, general manager, IT staffing at TeamLease Services. Most of the machine learning talent pool is spread across five cities: Bangalore, Chennai, Hyderabad, Mumbai/Pune belt and Delhi NCR region.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)